A process for making flexible circuits based on semiconducting carbon nanotube networks and high capacitance ion gel dielectrics through jet printing of liquid inks.
Mingjing Ha, Yu Xia, Alexander A. Green, Wei Zhang, Mike J. Renn, Chris H. Kim, Mark C. Hersam, C. Daniel Frisbie
Chemical Eng. and Materials Science , University of Minnesota, Materials Science and Eng. and Chemistry, Northwestern University, Electrical and Computer Eng., University of Minnesota, Optomec

Photolithographically pattern the source and drain contacts on a polyimide substrate or on an oxidized Si wafer (SiO2 - 300nm).
Electron beam evaporate Cr (2nm) and Au (28nm) respectively, to create the Source and Drain electrodes
Make a self assembled monolayer(SAM) on the Au electrodes: A: Polyimide substrate: Immerse in a 1mM ethanol solution of hexade-canethiol. B: SiO2 substrate: Immerse in Anthracene thiol for 12h.
Immerse the substrate into neat ethanol for 30 min, rinsed with ethanol then dried under flowing N2.
Print water based CNT ink on the channel area with a printing speed of 3mm/s or 5mm/s for low-coverage films.
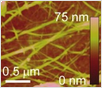
Rinse the substrate with deionized water to remove sodium cholate and allow to dry at 105oC for 1h.
Print the ion gel ink.
Print, while aligning with the channel, the PEDOT:PSS gate electrode, extended to an Au pad outside the channel for connection.
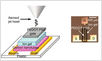
Heat the completed thin film transistor(TFT) to 105oC for 1h in a glovebox to remove residual solvent and water
Semiconducting CNT inks:
Water-based sorted CNT inks were prepared by density ultracentrifugation using arc-discharge grown CNTs from Carbon Solutions, Inc. The purity level of the CNTs was determined using optical absorbance spectroscopy. The sorted CNT inks were dialyzed into 0.2% w/v Sodium Cholate aqueous solution to remove the density medium iodixanol and also to lower the surfactant levels.
Ion Gel Ink:
The ion gel ink was a mixture of 1.5 wt% of triblock copolymer poly(styrene-b-methylmethacrylate-b-styrene) (PS-PMMA-PS) (Mn8.9k67k8.9k, polydispersity 1.17) and 8.5 wt% of ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsul-fonyl)imide ([EMIM][TFSI]) (from Merck) and 90 wt% ethyl acetate.
PEDOT:PSS ink:
(PH 500, 11.4 wt% polymer in water, from H.C. Stark), diluted with 10% by volume of ethyleneglycol to enhance the conductivity.
- Polyimide substrate
- Oxidized Silicon wafer
- Chromium
- Gold
- Hexade-Canethiol
- Anthracene thiol
- Ethanol
- Water-based semiconducting carbon nanotube(CNT) ink
- Ion gel ink
- Poly-(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):Poly(StyreneSulfonic acid) (PEDOT:PSS) ink
- Fume hood, Glovebox
- Mask aligner
- E-beam evaporator
- Aerosol jet printing system (Optomec, Inc.)
- Hotplate/oven
