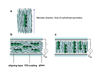
The anisotropic order of the LC platform imparts order onto the nano-size QDs, along the average orientational direction of the LC molecules. Because this direction can be aligned by external electric fields, the nanoscale assemblies of the QDs in the LC can be manipulated.
Understanding the interaction of nanoparticles with an LC and the principles governing their assembly through an LC mediated interactions is an important and active area of research with applications in next generation photonic devices, QD displays, biomedical imaging, and quantum computation.
Basu and Iannacchione were the second place student poster winners at the Nanomanufacturing Summit 2009, held in Boston from May 27 - 29 of this year.
Image: Schematic diagrams of cylindrial alignment of LC molecules and QD self-assembly in the nematic matrix.
Reproduced from Basu R and Iannacchione GS. 2009. Evidence for directed self-assembly of quantum dots in a nematic liquid crystal. Physical Review E – Rapid Communication, 80, 010701 (2009). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.80.010701. Permission pending.
